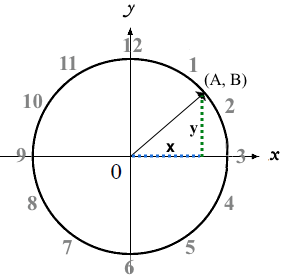
A unit clock (shown below) has a radius of 1, and is centered at the origin (0, 0). As time passes, the point (A, B) rotates around the circle.
A and B, around the clock
1 The line connecting (A,B) to the origin is the hypotenuse of a right triangle. How long is this line, no matter what time it is?
The tables below show the values of A (left table) and B (right table) at different times.
2 The values for 12, 3, and 6 o’clock are already shown in the tables below. Fill in the values of A and B at 9 o’clock.
|
|
|
3  On the unit clock above (and the right triangle to the right) the hand is pointing to (A, B) at 1:30, when A = B. Calculate the lengths of A and B in the space below. Then label them on the right triangle diagram.
On the unit clock above (and the right triangle to the right) the hand is pointing to (A, B) at 1:30, when A = B. Calculate the lengths of A and B in the space below. Then label them on the right triangle diagram.
A2 + B2 = 1 and A = B, so…
4 Fill in the rest of the table with values of A and B at 4:30, 7:30, and 10:30.
A and B, over time
5 In the graph below, draw a dot for the coordinates (time, A) in each row of the table. Connect them from left-to-right, to form a curve.
6 In the graph below, draw a star for the coordinates (time, B) in each row of the table. Connect them from left-to-right, to form a curve.

Unit Clock Starter File
Open the Unit Clock Starter File. The questions below refer to the animation you’ll see when you click "Run"
7 The green curve measures…
8 The blue curve measures…
These materials were developed partly through support of the National Science Foundation, (awards 1042210, 1535276, 1648684, 1738598, 2031479, and 1501927).  Bootstrap by the Bootstrap Community is licensed under a Creative Commons 4.0 Unported License. This license does not grant permission to run training or professional development. Offering training or professional development with materials substantially derived from Bootstrap must be approved in writing by a Bootstrap Director. Permissions beyond the scope of this license, such as to run training, may be available by contacting contact@BootstrapWorld.org.
Bootstrap by the Bootstrap Community is licensed under a Creative Commons 4.0 Unported License. This license does not grant permission to run training or professional development. Offering training or professional development with materials substantially derived from Bootstrap must be approved in writing by a Bootstrap Director. Permissions beyond the scope of this license, such as to run training, may be available by contacting contact@BootstrapWorld.org.